🌍 Understanding Google Cloud Regions, Zones & Cluster
If you’re getting started with Google Cloud Platform (GCP), one of the first things you’ll need to understand is Regions and Zones. These are the backbone of how GCP organizes and deploys resources worldwide.
Let’s break it down in simple terms. 🚀
🗺 What is a Region?
A Region is a geographical location where Google Cloud resources live.
Think of it like a city where your cloud data center is located.
Examples:
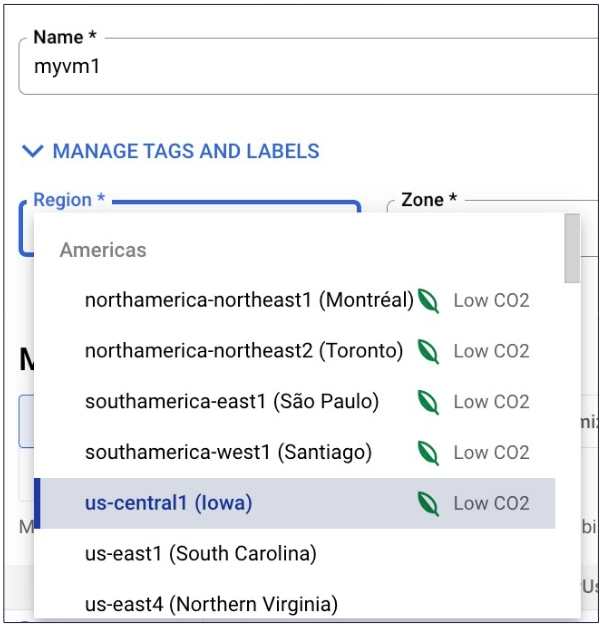
- us-central1 → Iowa
- us-east1 → South Carolina
- us-east4 → Northern Virginia
💡 Why Do We Need Regions?
- High Availability → Deploy workloads across multiple regions to ensure uptime.
- Compliance → Meet local data residency laws for specific countries/regions.
- Low Latency → Host apps closer to customers for faster performance.
📌 Where Do We Use Regions in GCP?
As a cloud admin, you choose a region when creating resources such as:
- VM instances
- Cloud SQL databases
- Storage buckets
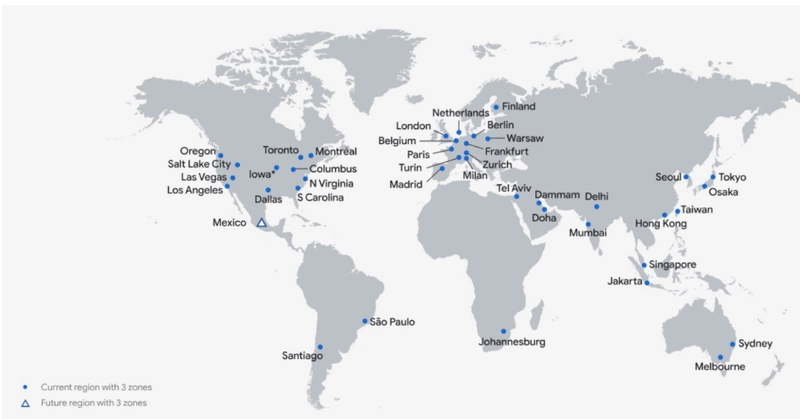
🌏 How Many Regions Does Google Cloud Have?
Currently, Google Cloud has 40+ regions (and growing!).
You can check the updated list here:
🗂 What is a Zone?
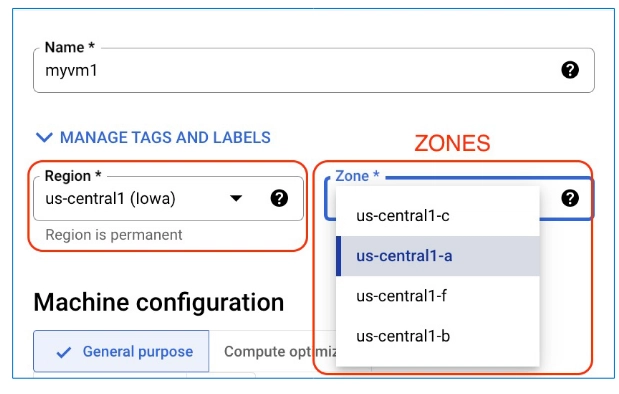
A Zone is a deployment area within a Region.
Each region typically has 3 or more zones.
Why multiple zones?
- Fault tolerance → If one zone goes down, others keep running.
- Low-latency interconnect → Zones within a region have high-speed links.
How are zones connected in a region ?
Zones are connected with low-latency links (Network performance will be very high in between zones)
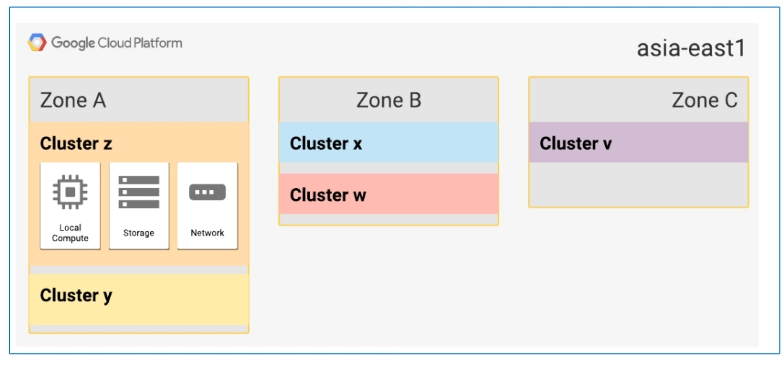
🖥 What Are Clusters in a Zone?
Inside each zone, there are clusters — sets of physical infrastructure (compute, networking, storage) in a data center.
Example Mapping:
- Organization A in asia-east1-a → Cluster Z
- Organization B in asia-east1-a → Cluster Y
Google ensures all projects in your organization follow a consistent zone-to-cluster mapping for predictability.
Zone to Cluster Mapping is not visible to customers. Google Cloud manages it internally
🔍 Summary
| Concept | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Region | Geographical location for resources | us-central1 |
| Zone | Subdivision inside a region | us-central1-a |
| Cluster | Physical hardware inside a zone | Cluster Z |