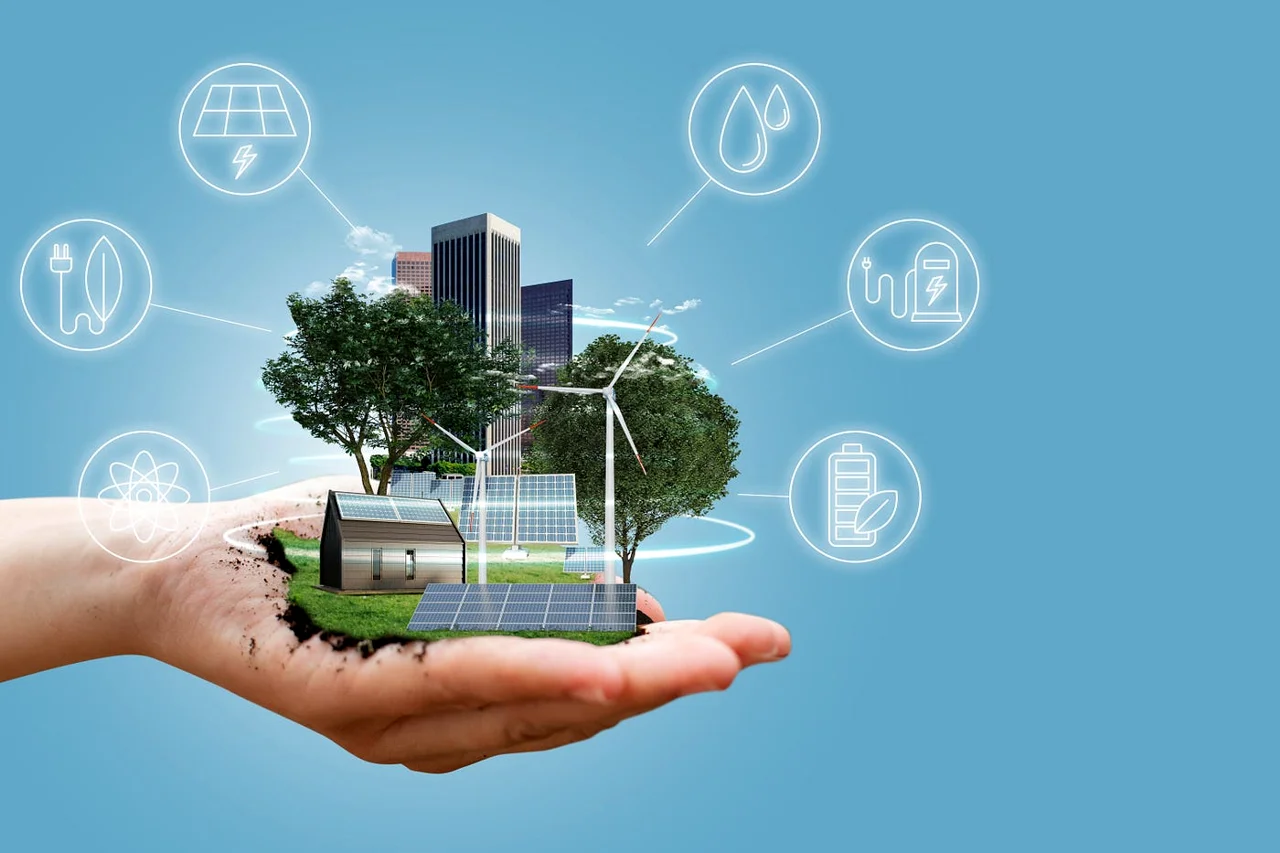
Sustainable Technology & Clean Energy Innovations: Powering a Greener Future
Introduction
As the world grapples with the consequences of climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation, the need for sustainable solutions has become more urgent than ever. Among the most promising responses are sustainable technologies and clean energy innovations. These advancements aim not only to reduce our carbon footprint but also to promote economic resilience, energy independence, and social equity. This blog will explore the current landscape, emerging trends, and future prospects of sustainable technology and clean energy, highlighting key innovations that are reshaping industries and lifestyles across the globe.
Understanding Sustainable Technology
Sustainable technology refers to innovations designed with environmental considerations in mind. These technologies are engineered to minimize negative impacts on the planet while supporting economic and social development. They often involve renewable resources, increased energy efficiency, and materials that can be reused or recycled. Sustainable technologies span various sectors, including transportation, construction, agriculture, and energy.
The Core of Clean Energy
Clean energy, a subset of sustainable technology, refers to energy derived from renewable, zero-emissions sources. It encompasses solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass energy. Clean energy is vital in the global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition away from fossil fuels, which are the primary contributors to global warming.
Key Innovations in Sustainable Technology
1. Smart Grids
Smart grids are modernized electrical grids that use digital communication technology to detect and react to local changes in usage. They improve efficiency, reliability, and sustainability by integrating renewable energy sources, enabling real-time energy management, and reducing waste.
2. Energy Storage Solutions
One of the main challenges of renewable energy is its intermittent nature. Energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, and emerging solid-state batteries, are essential for storing excess energy generated during peak production times for use during periods of low generation.
3. Green Building Technologies
Green buildings are constructed using environmentally responsible and resource-efficient processes. Innovations include energy-efficient HVAC systems, smart lighting, sustainable insulation materials, and advanced water-saving fixtures. LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification systems help standardize and promote these practices.
4. Sustainable Agriculture Technologies
Precision farming, vertical farming, and aquaponics are transforming agriculture. These technologies reduce water and fertilizer usage, lower emissions, and enhance crop yields. They also support local food production, which decreases the carbon footprint associated with food transport.
5. Electric and Hydrogen-Powered Vehicles
The transportation sector is undergoing a major shift with the advent of electric vehicles (EVs) and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Companies like Tesla, Rivian, and Toyota are pushing the boundaries of battery technology, while governments invest in charging infrastructure and incentives.
Clean Energy Innovations Driving Change
1. Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Technology
Solar PV panels convert sunlight into electricity. Innovations in panel efficiency, flexible solar materials, and solar glass are making solar energy more accessible and cost-effective. Community solar projects and solar leasing models are also expanding access.
2. Wind Energy Advancements
Wind power has grown significantly, with turbines becoming larger and more efficient. Offshore wind farms, particularly in Europe and Asia, are helping countries meet their renewable energy targets. Floating wind turbines are expanding the geographic scope of wind energy.
3. Hydroelectric Innovations
Small-scale hydro and run-of-the-river systems are being developed to reduce the environmental impact of traditional large dams. Pumped-storage hydro is also a key player in grid energy storage.
4. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal power harnesses heat from beneath the Earth’s surface. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) and direct-use applications are expanding the potential of this reliable energy source.
5. Biomass and Bioenergy
Bioenergy includes electricity, heat, and fuels derived from organic materials. Second-generation biofuels made from non-food biomass are gaining traction, reducing competition with food production and land use.
Policy and Investment
Government policies and private investment play a crucial role in advancing sustainable technology and clean energy. International agreements like the Paris Accord, along with national incentives, tax credits, and carbon pricing mechanisms, are encouraging innovation and adoption. Venture capital and green bonds are financing startups and large-scale projects alike.
Challenges and Barriers
Despite progress, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of sustainable technology:
- High upfront costs
- Lack of infrastructure
- Regulatory hurdles
- Public awareness and resistance to change
Addressing these barriers requires coordinated efforts among governments, businesses, and communities.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data
AI and big data are revolutionizing sustainable practices. In energy, AI predicts demand, optimizes grid operations, and manages distributed energy resources. In agriculture, data analytics improve crop yields and reduce waste. Predictive maintenance powered by AI extends the life of renewable energy systems, improving ROI and reducing downtime.
Global Impact and Case Studies
Countries around the world are embracing clean energy:
- Germany’s Energiewende (energy transition) aims for a nearly carbon-neutral economy.
- China leads the world in solar panel manufacturing and electric bus deployment.
- Costa Rica regularly runs on 100% renewable energy for extended periods.
- India is rapidly expanding its solar capacity through large-scale solar parks.
The Future of Sustainable Technology
Emerging trends suggest a bright future:
- Fusion energy research could provide limitless clean power.
- Perovskite solar cells offer higher efficiency at lower cost.
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS) could allow continued use of fossil fuels with reduced emissions.
- Green hydrogen could revolutionize industry, transportation, and storage.
Conclusion
Sustainable technology and clean energy innovations are no longer optional—they are imperative. They offer a pathway to a more equitable, resilient, and environmentally sound future. Through continued investment, research, and global cooperation, we can accelerate the transition to a world powered by clean, renewable energy. As consumers, businesses, and policymakers unite in this effort, the potential for transformative change has never been greater. The time to act is now.
By embracing these innovations today, we can ensure a cleaner, brighter tomorrow for generations to come.