AWS open source newsletter, #212
Edition #212 – July 2025
Welcome to issue #212 of the AWS open source newsletter, the newsletter where I try and provide you the best open source on AWS content. This newsletter was started in January 2021, and since then over you have engaged in the projects and content I put together over 3 million times. Amazing, so thank you for those of you who are still following and still sending me messages of support.
As always, this edition has more great new projects to check out. In this edition, we have a nice selection of projects to help you work with your data in Amazon S3, a new innovation framework, a security assessment tool, a tool for orchestrating CDK resources across AWS accounts, and the usual selection of generative AI demos across Strands Agents, the recently launched Amazon Bedrock AgentCore, and Model Context Protocol (MCP)servers. The projects will keep you busy until next month for sure, but we also have plenty of reading material in this months newsletter. In this edition we have featured projects that include Valkey, Strands Agents, Kubernetes, Apache Spark, AWS CDK, ArgoCD, PostgreSQL, Ray, Apache Cassandra, Apache Kafka, RabbitMQ, Amazon Corretto, Gremlin, openCypher, MLFlow, AWS Neuron, AWS IoT Greengrass, and Amazon Q CLI.
Check out the list of contributors at the end of the newsletter, and as always, get in touch if you want me to feature your projects in this open source newsletter.
Latest open source projects
The great thing about open source projects is that you can review the source code. If you like the look of these projects, make sure you that take a look at the code, and if it is useful to you, get in touch with the maintainer to provide feedback, suggestions or even submit a contribution. The projects mentioned here do not represent any formal recommendation or endorsement, I am just sharing for greater awareness as I think they look useful and interesting!
Tools
aws-appsync-events-swift
aws-appsync-events-swift provides a Swift library to interact with AWS AppSync Events API in your Apple iOS, macOS and tvOS applications.
agent-dev-toolkit
agent-dev-toolkit or Agent Development Toolkit (ADT), provides a single command-line interface that lets developers build, test, and iterate on Strands agents with ease during local development. The CLI unifies agent execution, observability, UI, and local containerisation into one cohesive developer experience, enabling developers to iterate and experiment faster with immediate feedback loops and streamlined workflows. Check out the detailed README file for more info on how to get started with this command line tool.
sra-verify
sra-verify is a security assessment tool that automates the verification of AWS Security Reference Architecture (SRA) implementations across multiple AWS accounts and regions. It provides detailed findings and actionable remediation steps to ensure your AWS environment follows security best practices. The tool performs automated security checks across multiple AWS services including CloudTrail, GuardDuty, IAM Access Analyzer, AWS Config, Security Hub, and S3. It supports multi-account environments and can run checks specific to management, audit, and log archive accounts while providing detailed findings with remediation guidance. Jeremy Schiefer, Justin Kontny, **and **Matt Nispel have put together a blog post that provides more info about this project, so check out Introducing SRA Verify – an AWS Security Reference Architecture assessment tool
innovation-sandbox-on-aws
innovation-sandbox-on-aws – The Innovation Sandbox on AWS solution allows cloud administrators to set up and recycle temporary sandbox environments by automating the implementation of security and governance policies, spend management mechanisms, and account recycling preferences through a web user interface (UI). Using the solution, customers can empower their teams to experiment, learn, and innovate with AWS services in production-isolated AWS accounts that are recycled after use.
You can find out more, including a detailed implementation guide by checking out the homepage, Innovation Sandbox on AWS
s3vectors-embed-cli
s3vectors-embed-cli is a standalone command-line tool that simplifies the process of working with vector embeddings in S3 Vectors. You can create vector embeddings for your data using Amazon Bedrock and store and query them in your S3 vector index using single commands. This tool facilitates semantic similarity search on media in Amazon S3 via AWS Bedrock and Amazon S3 Vectors. Check out the README for the supported commands, installation and configuration details as well as some quick starts to help you understand how this all works.
Also, good to know – Amazon S3 Vectors Embed CLI is in preview release and is subject to change.
s3grep
s3grep is the latest essential tool from Damon Cortesi that provides a parallel CLI tool for searching logs and unstructured content in Amazon S3 buckets. It supports .gz decompression, progress bars, and robust error handling—making it ideal for cloud-native log analysis.
s3-vectors-mcp
s3-vectors-mcp hot off the announcement from the AWS Summit New York, AWS Community Hero Kazuaki Morita has put together this repo that provides tools for interacting with AWS S3 Vectors service. This server enables AI assistants to embed text using Amazon Bedrock models and store/query vector embeddings in S3 Vectors indexes. Check out the README for details of the specific features as well as how to configure this MCP Server.
amazon-datazone-mcp-server
amazon-datazone-mcp-server repo provides a high-performance Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that provides seamless integration with Amazon DataZone services. This server enables AI assistants and applications to interact with Amazon DataZone APIs through a standardised interface.
robinzhon
robinzhon is a high-performance Python library from Robin Quintero for fast, concurrent S3 object downloads. Check out the README for details on how to get started. Robin shared why he createdthis project:
Recently at work I have faced that we need to pull a lot of files from S3 but the existing solutions are slow so I was thinking in ways to solve this and that’s why I decided to create robinzhon. The main purpose of robinzhon is to download high amounts of S3 Objects without having to do extensive manual work trying to achieve optimizations. I know that you can implement your own concurrent approach to try to improve your download speed but robinzhon can be 3 times faster even 4x if you start to increase the max_concurrent_downloads but you must be careful because AWS can start to fail due to the amount of requests.
bedrock-agentcore-sdk-python
bedrock-agentcore-sdk-python is the public preview of the Bedrock AgentCore SDK. Amazon Bedrock AgentCore, a comprehensive set of enterprise-grade services that help developers quickly and securely deploy and operate AI agents at scale using any framework and model, hosted on Amazon Bedrock or elsewhere. Check out my colleague Danilo’s blog post to find out more, Introducing Amazon Bedrock AgentCore: Securely deploy and operate AI agents at any scale (preview)
bedrock-agentcore-starter-toolkit
bedrock-agentcore-starter-toolkit provides a CLI toolkit for deploying AI agents to Amazon Bedrock AgentCore. Zero infrastructure management with built-in gateway and memory integrations. This is currently in public preview, so subject to breaking changes – so bear that in mind when you try this out.
nova-prompt-optimizer
nova-prompt-optimizer is a Python SDK for optimising prompts for Nova. Looks very comprehensive, so worth checking out the README. Again, public preview folks so bear this in mind.
langgraph-aws-deployment
langgraph-aws-deployment this repo from Ali mz provides a script that simplifies deploying langgraph on yuor AWS environments. If you just want to kick the tires on an agent without managing EC2 or writing Terraform, this gets you from git clone to a public HTTPS endpoint in ~10 min. It’s opinionated (Fargate, ALB, Parameter Store) but easy to tweak. The author is looking for feedback, bug reports, and PRs. Make sure to give it a ⭐ if you find it useful.
terraform-provider-mongodb
terraform-provider-mongodb is new repo from AWS Community Builder Anuj Tyagi that provides a new custom Terraform/OpenTofu provider for working with DocumentDB (as well as MongoDB). Anuj has also put together a nice post that looks at the motivation for building this and how you can get started, so check out Automate DocumentDB Operations using custom Terraform provider if this sounds like something useful to you.
kiro-steering-docs
kiro-steering-docs is a new repo from AWS Hero Matthew Bonig that shares Kiro steering files that are helpful for providing more concise and accurate responses when using AI Coding Assistants, in this case Kiro but they might work in other tools too.
orbits
orbits is an open-source framework for orchestrating long-lived resources and workflows involving long-running processes. It lets you manage your infrastructure templates from a single, unified place using native TypeScript code. By combining the flexibility of Node.js with a powerful workflow engine, Orbits helps you build modern, adaptable infrastructure operations. It’s ideal for automating processes that self-adapt to their environment and for exposing workflows as reusable, reliable building blocks. It also provides a solid foundation for building crash-resilient Node.js applications. Louis Dussarps provides you with a real use case of how you can use this tool in the blog post, Solving cross-account resources for AWS CDK
the-cloud-scroll
the-cloud-scroll is a project that provides comprehensive, gamified AWS learning platform that makes mastering cloud computing engaging and accessible, that you are able to customise for your own use. Built with Amazon Q CLI assistance, and there is a hosted version of the app so you can try before you build.
Demos, Samples, Solutions and Workshops
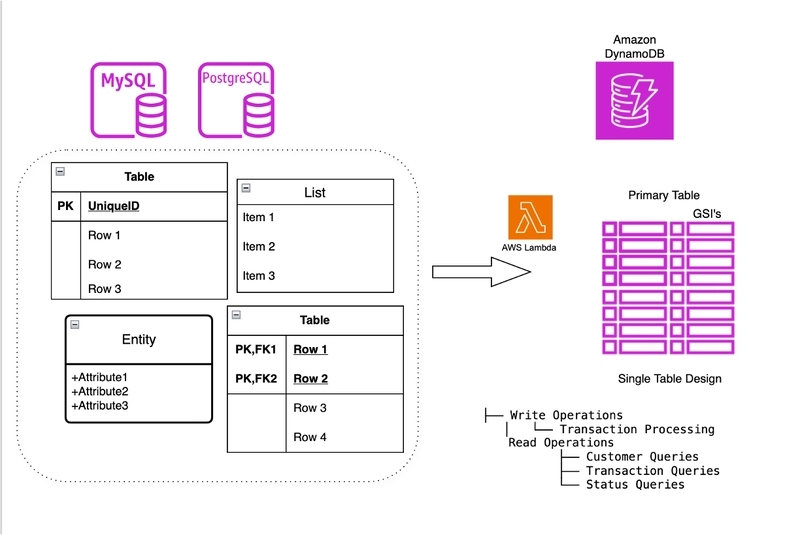
sample-design-dynamodb-datamodel
sample-design-dynamodb-datamodel provides a data modelling solution for Amazon DynamoDB that simplifies working with single-table design patterns. This repository contains CloudFormation templates and code examples for implementing efficient DynamoDB data models.
dynamodb-stream-to-dsql
dynamodb-stream-to-dsql is a nice demo from AWS Hero Lee Gilmore that provides an example of streaming data changes (CDC) from Amazon DynamoDB to Amazon Aurora DSQL. Make sure you read the accompanying blog post, Amazon Aurora DSQL Sidecar to DynamoDB — Part 1, where Lee unpacks some of the use cases where this pattern and approach might be useful.
strands-agent-on-lambda
strands-agent-on-lambda this repo contains a sample implementation of user-aware AI Agent and MCP Server running on AWS Lambda. The sample implements an AI-based Travel Agent for a fictitious corporation AcmeCorp.
strands-a2a-demo
strands-a2a-demo this repo provides a demo that showcases multiple AI agents using the complete official A2A (agent-to-agent) Python SDK patterns from google-a2a/a2a-samples. The agents use the Strands Agents Python SDK for their LLM implementation, fully integrated with the official A2A SDK patterns. This project features a unified a2a-client with multiple modes of operation, including web-based UI, voice interaction capabilities, and comprehensive testing.
a2a-advisory-trading
a2a-advisory-trading is a comprehensive demo of a serverless multi-agent trading advisory system built on AWS, leveraging Google’s Agent2Agent Protocol using a2a SDK, Strands Agent, and built-in MCP tools from Strands SDK to deliver personalized investment analysis, risk assessment, and secure trade execution. This project serves as a reference implementation demonstrating how to design and deploy multi-agent systems using Google’s Agent2Agent Protocol on AWS through a serverless architecture, powered by Strands Agent and Amazon Bedrock. It showcases patterns for building agent networks while leveraging cloud-native services. The README provides all the questions you are probably asking yourself right now….
nova_virtual_stylist
nova_virtual_stylist provides a super fun demo that showcases the power Amazon Nova Canvas and Nova Reel that allows you to upload your photo and clothing items (or generate them with AI), and then see how they look with virtual try-on, then create stunning fashion videos to showcase your style. I have seen this project in action, and its pretty cool so defo add this to your list of projects to try out.
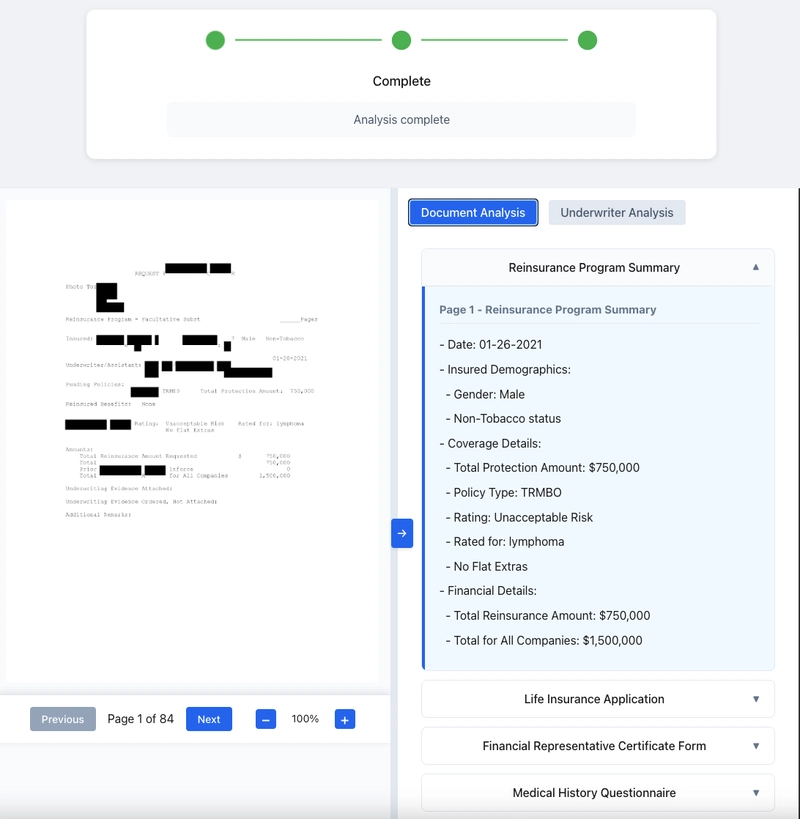
sample-genai-underwriting-workbench-demo
sample-genai-underwriting-workbench-demo a demonstration project showcasing the power of Amazon Bedrock and Claude 3.7 Sonnet in transforming life insurance underwriting workflows. This solution leverages intelligent document processing to streamline the underwriting process by automatically extracting, analyzing, and making accessible critical information from insurance applications and related documents.
AWS and Community blog posts
This weeks essential reading
Here are the posts that I think are essential reads, so start here. We have more than we usually do, but thought these were all essential reads this month.
-
Year One of Valkey: Open-Source Innovations and ElastiCache version 8.1 for Valkey – a retrospective of a year of Valkey, and how support for this open source project has grown from strength to strength
-
Introducing Strands Agents 1.0: Production-Ready Multi-Agent Orchestration Made Simple – is the first of a series of posts that looks at Strands Agents, an open source SDK that takes a model-driven approach to building and running AI agents in just a few lines of code that can scale from simple to complex agent use cases, and from local development to deployment in production hands on
-
Post-quantum TLS in Python – looks at how you can test Post-quantum TLS in Python applications with boto3 and other Python libraries, that will help protect your applications against potential quantum computer (CRQC) attacks
Community
Each month I spend time reading posts from across the AWS community on open source topics. In this section I share what personally caught my eye and interest, and I hope that many of you will also find them interesting.
This month we start off with AWS Community Builder Ukeme David Eseme who shares his experiences deep in the trenches of Kubernetes land, and walks you through the lessons learned upgrading a large Kubernetes infrastructure from v1.26 to v1.33 in the post, How I Survived the Great Kubernetes Exodus: Migrating EKS Cluster from v1.26 to v1.33 on AWS. If you are spending any time looking after Kubernetes, this is a must read post. AWS Hero Arshad Zackeriya continues the Kubernetes theme in his post, Cross Account Access with EKS Pod Identity that is a great read if you want to know more about how your Kubernetes resources gain access to AWS resources. To complete this Kubernetes round up, I enjoyed this deep dive from the Pintrest Engineering team, Next Gen Data Processing at Massive Scale At Pinterest With Moka (Part 1 of 2). It talks about how they built an optimised data processing platform on Kubernetes, called Moka. Grab a cup of your favourite beverage before sitting down to read this one. Great stuff, and look out for part two when its published.
From Kubernetes we move to Strands Agents, an open source SDK that takes a model-driven approach to building and running AI agents in just a few lines of code. AWS Community Builder Davide De Sio took time to add the third in a series of posts, sharing how to add guardrails to your Strands Agents (and how simple it is). Go check out the post, Add guardrails to your Strands Agent in zero time with Amazon Bedrock Guardrails (and if you missed the others, check those out too). Following Davide, AWS Community Builder Vivek V put together Agent-to-Agent AI Integration: AWS Security Analysis with AI21 Maestro & Strands Agents that demonstrates agent-to-agent AI orchestration to help optimise AWS security analysis, combining AI21 Maestro’s requirement-driven validation with Strands Agents through the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
To finish up this month’s community round up we have a number of posts AWS CDK fans. It was good to see so many excellent community articles this month. AWS Hero Kenta Goto gets us going with How to Use AWS CDK Stage and When to Choose Static vs Dynamic Stack Creation which is a great read if you are wondering how you should approach sharing your CDK stacks across different AWS environments. Next is AWS Community Builder Moya Richards who explores something I didn’t know about (cdk-triggers), covering what they are, some sample use cases before going in with some code examples. If this sounds of interest, dive into the post, Automate Post-Deployment Tasks with cdkTrigger in AWS CDK. The final CDK post comes from AWS Community Builder Matheus das Mercês who is telling you, You Don’t Need a Construct for That: Best Practices for Serverless Infrastructure with AWS CDK Blueprints, providing you with an overview of the different CDK building blocks, and share some good current practices to help you along the way.
If you have an open source article you want to share with the community, drop me a message (LinkedIn, or via ricsue@amazon.co.uk and I will be sure to check it out.
Cloud Native
- Deep dive into cluster networking for Amazon EKS Hybrid Nodes – walks you through detailed steps for setting up the cluster networking for Amazon EKS Hybrid Nodes, exploring a number of different CNI and load balancing solutions for various use cases and scenarios [hands on]
- Implement monitoring for Amazon EKS with managed services – shows you how to implement comprehensive monitoring for Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) workloads using AWS managed open source services [hands on]
- Scaling beyond IPv4: integrating IPv6 Amazon EKS clusters into existing Istio Service Mesh – provides a step-by-step guide for combining IPv6-enabled EKS clusters with your existing Istio Service Mesh and IPv4 workloads, enabling a graceful transition to IPv6 on AWS [hands on]
- GitOps continuous delivery with ArgoCD and EKS using natural language – explores how to use Amazon Q CLI together with Model Context Protocol (MCP) to transforming complex Kubernetes operations into simple conversational interactions [hands on]
Data and Analytics
- Introducing Enhanced JSON Capabilities in Valkey – guides you through setting up the Valkey JSON module and demonstrate how to use it for some common workloads [hands on]
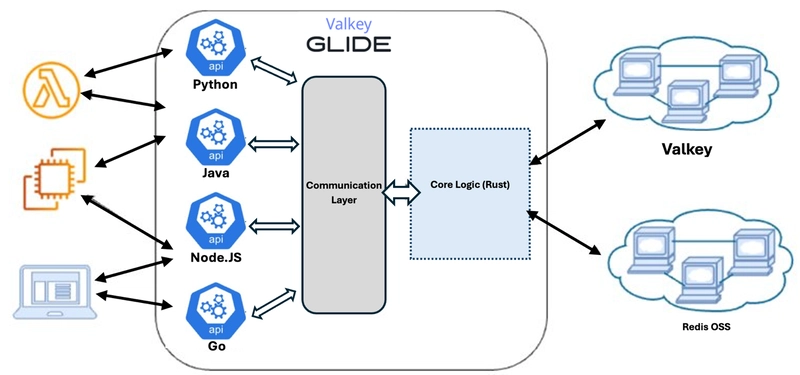
- Announcing Valkey GLIDE 2.0 with support for Go, OpenTelemetry, and batching – looks at the next generation client for Valkey, GLIDE 2.0 covering why it was created and then providing examples of how to use it [hands on]
- Compaction support for Avro and ORC file formats in Apache Iceberg tables in Amazon S3 – examines the performance benefits of automatic compaction of Iceberg tables using Avro and ORC file types in S3 Tables for a data ingestion use with over 20 billion events [hands on]
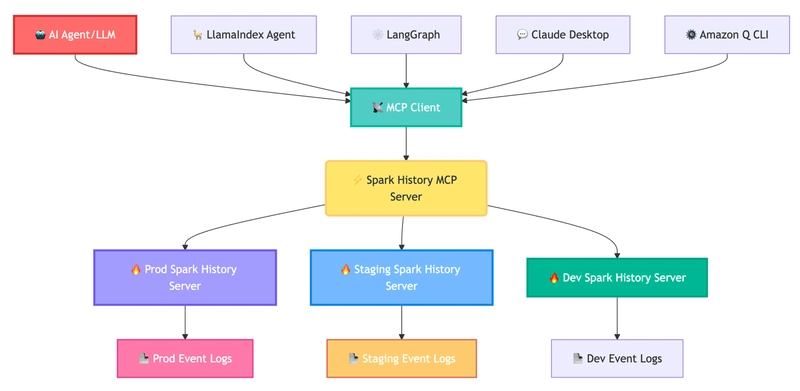
- Introducing MCP Server for Apache Spark History Server for AI-powered debugging and optimization – shows you how to get started with the new open source MCP Server that will help you use generative AI tools like Amazon Q Developer to simplify performance troubleshooting and optimisation by examining your Apache Spark History Server [hands on]
- Volatility classification in PostgreSQL – dives deep into how properly categorising functions as VOLATILE, IMMUTABLE, or STABLE allows PostgreSQL’s optimiser to make informed decisions, leading to more efficient query plans [hands on]
- Fully Sharded Data Parallel with Ray on Amazon ECS – looks at how you can use model sharding techniques such as Fully Sharded Distributed Data Parallel (FSDP) on Amazon ECS that will help you to optimise your costs to run training for models with billions of parameters [hands on]
-
Use AWS FIS to test the resilience of self-managed Cassandra – reviews how you can use AWS FIS to craft a chaos experiment to test the resilience of your self-managed Cassandra clusters running on Amazon EC2 [hands on]
-
Overcome your Kafka Connect challenges with Amazon Data Firehose – shows how Amazon Data Firehose provides a straightforward way to deliver data from Apache Kafka to Amazon S3, enabling you to save costs and reduce latency to seconds [hands on]
-
Building serverless event streaming applications with Amazon MSK and AWS Lambda – explores how to simplify your event-driven application architecture using AWS Lambda with Apache Kafka, showing how to configure Lambda as a consumer for Kafka topics, including a cross-account setup and then how to optimise price and performance for these applications [hands on]
Other posts to check out
- Preview Release of the AWS SDK Java 2.x HTTP Client built on Apache HttpClient 5.5.x – provides details of the new AWS SDK for Java 2.x that introduces the Apache 5 SDK HTTP client which is built on Apache HttpClient 5.5.x [hands on]
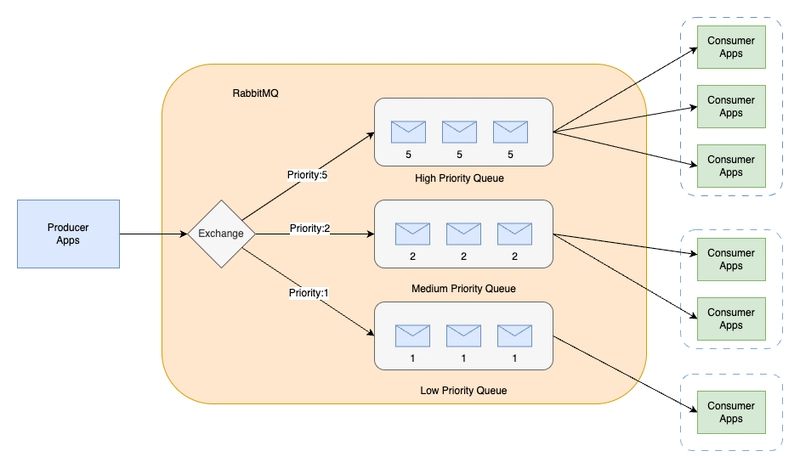
- Implementing message prioritization with quorum queues on Amazon MQ for RabbitMQ – describes the different approaches to implementing message prioritisation in quorum queues in Amazon MQ for RabbitMQ [hands on]
- Improve RabbitMQ performance on Amazon MQ with AWS Graviton3-based M7g instances – is a quick post that looks at benchmarks comparing performance and cost characteristics when using AWS Graviton based instances for your Amazon MQ infrastructure
Quick updates
Amazon Corretto
On July 15, 2025 Amazon announced quarterly security and critical updates for Amazon Corretto Long-Term Supported (LTS) and Feature Release (FR) versions of OpenJDK. Corretto 24.0.2, 21.0.8, 17.0.16, 11.0.28, 8u462 are now available for download. Amazon Corretto is a no-cost, multi-platform, production-ready distribution of OpenJDK.
Kubernetes
Amazon EKS announced support for up to 100,000 worker nodes in a cluster, enabling you to run ultra scale AI/ML training and inference workloads in a single cluster. With Amazon EC2’s new generation accelerated computing instance types, 100,000 worker nodes support up to 1.6 million Trainium chips with Trn2 instances and 800,000 NVIDIA GPUs with P5 and P6 instances in a single cluster. This enables you to run ultra scale AI/ML workloads that require all compute accelerators to be available within a single cluster, as these workloads cannot be easily distributed across multiple clusters.
There were a couple of great blog posts that looked at this in more details. Starting off with Under the hood: Amazon EKS ultra scale clusters which looks under the hood and provides copious amounts of graphs. After reading that check out Amazon EKS enables ultra scale AI/ML workloads with support for 100K nodes per cluster which looks at some of the ways you might be able to use that scale.
Valkey
Amazon ElastiCache announced support for Valkey 8.1, bringing the latest innovations from the Valkey open source project into ElastiCache for Valkey, including new capabilities, performance improvements, and observability enhancements. These improvements will help developers to increase an application’s responsiveness while reducing infrastructure cost for in-memory workloads.
Amazon ElastiCache version 8.1 for Valkey introduces native support for Bloom filters, a new data type allowing you to perform lookups using as much as 98% less memory compared to using the Set data type. You can read more about this in the post, Implement fast, space-efficient lookups using Bloom filters in Amazon ElastiCache. It also includes a new hash table implementation that improves throughput by up to 10% when using pipelining and reduces memory overhead to lower memory usage by as much as 20% for common key/value patterns. This new release also introduces a new COMMANDLOG feature that records large requests and replies, improving visibility of end-to-end latency and enabling you to optimise traffic patterns or troubleshoot unexpected usage spikes.
PostgreSQL
Several updates for folks interested in PostgreSQL.
First up is news that Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL 18 Beta 2 is now available in the Amazon RDS Database Preview Environment, allowing you to evaluate the pre-release of PostgreSQL 18 on Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL. You can deploy PostgreSQL 18 Beta 2 in the Amazon RDS Database Preview Environment that has the benefits of a fully managed database. PostgreSQL 18 includes “skip scan” support for multicolumn B-tree indexes and improves WHERE clause handling for OR and IN conditions. It introduces parallel GIN index builds and updates join operations. Observability improvements show buffer usage counts and index lookups during query execution, along with per-connection I/O utilisation metric
Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition has added support for PostgreSQL versions 17.5, 16.9, 15.13, 14.18, and 13.21. The update includes PostgreSQL community’s product improvements and bug fixes, while introducing Aurora-specific enhancements: read replica optimisations to reduce downtime during cluster upgrades, new features for Babelfish, and security improvements.
To finish up this roundup is news that Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition now supports a maximum storage limit of 256 TiB, doubling the previous limit of 128 TiB. This enhancement allows customers to store and manage even larger datasets within a single Aurora database cluster simplifying data management for large-scale applications and supporting the growing data needs of modern applications. Customers only pay for the storage they use, with no need for upfront provisioning of the full 256 TiB. To access the increased storage limit, upgrade your cluster to supported database versions. Once upgraded, Aurora storage will automatically scale up to 256 TiB capacity based on the amount of data in the cluster volume.
Gremlin and openCypher
Graph Explorer provides a React-based web application that enables users to visualise both property graph and RDF data and explore connections between data without having to write graph queries. You can connect to a graph database over HTTP that supports the W3C RDF/SPARQL open standard, the openCypher open source specification, or the open source Apache TinkerPop Gremlin.
Launched this month is a new feature in Graph Explorer that enables users to write and execute native Gremlin and openCypher queries directly within the interface. This enhancement empowers data scientists, developers, and database administrators to seamlessly interact with their graph databases using their preferred query language, eliminating the need for additional tools or interfaces. With this update, users can now leverage the full expressive power of both Gremlin and openCypher to traverse complex relationships, perform advanced pattern matching, and extract valuable insights from their graph data while enjoying the intuitive visual environment of Graph Explorer.
Apache Kafka
A couple of nice updates this month.
First up is news about the Amazon MSK announces a model-context protocol (MCP) based server that allows customers to interact with their Amazon MSK clusters using a standardised natural language interface and agentic applications. Amazon MSK’s MCP server uses Anthropic’s open-source model-context protocol that standardises how AI-assisted agents interact with external systems, such as databases, knowledge sources, and other microservices. The server provides AI agents with aggregate views of cluster metrics, configuration states, and operational context, delivering built-in understanding of cluster quotas, capacity limits, best practice guidelines, and contextual recommendations based on workload characteristics. This approach enables agents to make informed decisions about cluster modifications with full awareness of constraints and dependencies. Additionally, each interaction is governed by the customer-defined security policies, which limits access to only those agents who have explicit permissions to the APIs required to achieve the desired objective. To download and try out the open-source MCP servers for these services locally with your AI-enabled IDE of choice, visit the aws-labs GitHub repository.
In other news, Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK) now supports up to 5x more partitions per Express Broker, improving price-performance by up to 50% for partition-bound workloads. Express Brokers are a broker type in Amazon MSK that provide up to 3x more throughput, up to 20x faster scaling, and up to 90% faster recovery compared to Standard Apache Kafka brokers. With this launch, partition-bound workloads can be hosted on fewer brokers. For example, m7g.16xlarge instances now support up to 20,000 partitions per broker vs 4,000 partitions previously. To further improve the resilience of your clusters, Amazon MSK now also now limits the maximum number of partitions that can be created per Express Broker. These quotas help maintain cluster stability by preventing partition counts from exceeding safe thresholds at these higher limits. The increased partition support is particularly valuable for streaming applications requiring numerous topics, micro-service architectures with many small topics, and data ingestion pipelines supporting multiple data sources among others.
Apache Cassandra
Amazon Keyspaces (for Apache Cassandra) is a scalable, highly available, and managed Apache Cassandra–compatible database service. Amazon Keyspaces (for Apache Cassandra) now supports Change Data Capture (CDC) streams, enabling you to capture row-level changes in your tables in near-real time. CDC streams in Amazon Keyspaces automatically capture insert, update, and delete operations as change events, delivering them in order with automatic deduplication. With CDC streams, you can build event-driven applications and implement use cases such as data analytics, text search, ML training/inference, and continuous data backups for archival.
CDC streams retain data for up to 24 hours and can scale automatically to match your workload, without requiring any infrastructure management. Additionally, enabling CDC streams will have no impact on your table capacity for compute or storage operations. To consume the CDC stream records, you can use either the Keyspaces Data Streams API or leverage the Kinesis Client Library, a java library that makes it easy to consume and process stream records.
Dive deeper by reading Introducing Amazon Keyspaces CDC streams.
MLflow
Amazon SageMaker now offers fully-managed support for MLflow 3.0 that streamlines AI experimentation and accelerates your GenAI journey from idea to production. This release transforms managed MLflow from experiment tracking to providing end-to-end observability, reducing time-to-market for generative AI development.
As customers across industries accelerate their generative AI development, they require capabilities to track experiments, observe behaviour, and evaluate performance of models and AI applications. Data scientists and developers lack tools for analysing the performance of models and AI applications from experimentation to production, making it hard to root cause and resolve issues. Teams spend more time integrating tools than improving their models or generative AI applications. With this launch, fully managed MLflow 3.0 on Amazon SageMaker AI enables customers to accelerate generative AI by making it easier to track experiments and monitor performance of models and AI applications using a single tool. Tracing capabilities in fully managed MLflow 3.0 enable customers to record the inputs, outputs, and metadata at every step of a generative AI application, helping developers quickly identify the source of bugs or unexpected behaviours. By maintaining records of each model and application version, fully managed MLflow 3.0 offers traceability to connect AI responses to their source components, allowing developers to quickly trace an issue directly to the specific code, data, or parameters that generated it. This dramatically reduces troubleshooting time and enables teams to focus more on innovation.
AWS Neuron
Neuron v2.24 is now available, delivering new features and performance improvements for customers building and deploying deep learning models on AWS Inferentia and Trainium-based instances. Neuron 2.24 introduces support for PyTorch 2.7, enhanced inference capabilities, and expanded compatibility with popular machine learning frameworks. These updates help developers and data scientists accelerate model training and inference, improve efficiency, and simplify the deployment of large language models and other AI workloads.
With Neuron 2.24, customers can take advantage of advanced inference features such as prefix caching for faster Time-To-First-Token (TTFT), disaggregated inference to reduce prefill-decode interference, and context parallelism for improved performance on long sequences. The release also brings support for Qwen 2.5 text models and improved integration with Hugging Face Optimum Neuron and PyTorch-based NxD Core backend.
AWS IoT Greengrass
AWS IoT Greengrass announced the release of AWS IoT Greengrass v2.15, introducing significant updates to both nucleus and nucleus lite core components. AWS IoT Greengrass is an Internet of Things (IoT) edge runtime and cloud service that helps customers build, deploy, and manage device software at the edge. The latest release, version 2.15, strengthens core capabilities with enhanced secret and log management, advancing both security posture and troubleshooting efficiency for IoT applications running at the edge. The new release also offers updates for AWS IoT Greengrass nucleus lite, a lightweight, open-source edge runtime, specifically designed for resource-constrained devices with minimal footprint (5MB RAM). The new nucleus lite release introduces Docker containers management, expanding capabilities of lightweight IoT deployments and delivering containerised applications support in resource-constrained environments.
Videos of the month
Behind the Code! How We Built Amazon Q Developer CLI in Rust
Amazon Q CLI is an open source, next generation developer tool that you use in the terminal. In this video my colleague Darko Mesaros is joined by Brandon Kiser show how Amazon Q CLI is built, why they chose Rust, and a look into the source code to figure out it’s internals!
The MCP Revolution: AWS Team’s Journey from Internal Tools to Open Source AI Infrastructure
The AWS PACE team share their journey from internal hackathon project to releasing 30+ open source MCP servers that are transforming how developers interact with AI assistants like Amazon Q Developer.
Build Your First Agent Workflow with Strands
This technical deep dive with Piyali Kamra explores the world of agentic AI using Strands Agents — an open source, modern, flexible framework that enables developers to orchestrate intelligent workflows faster than ever. The video looks at what Strands Agents are and how they operate within the broader agentic AI ecosystem. You’ll learn how to set up your development environment with minimal effort, and guides you through building a functional demo agent workflow from scratch using AWS tools. Along the way, we’ll share practical tips for scaling and customising your agents to suit a wide range of use cases.
Celebrating open source contributors
The articles and projects shared in this newsletter are only possible thanks to the many contributors in open source. I would like to shout out and thank those folks who really do power open source and enable us all to learn and build on top of what they have created.
So thank you to the following open source heroes: Damon Cortesi, Kazuaki Morita, Robin Quintero, Ali mz, Louis Dussarps, Matthew Bonig, Anuj Tyagi, Danilo Poccia, Banjo Obayomi, Piyali Kamra, Jinga Gandhi, Brandon Kiser, Darko Mesaros, Rajesh Kantamani, Shyam Jeedigunta, Apoorva Kulkarni, Raghav Tripathi, Mas Kubo, Madelyn Olson, Rain Valentine, Karthik Subbarao, Kannan Iyer, Cameron Zack, Jeremy Schiefer, Justin Kontny, Matt Nispel, Ryan Coleman, Belle Guttman, Darin McAdams, Elie Schoppik, Nick Aldridge, James Ward, Clare Liguori, John Viegas, Akhil Melakunta, Vinodh Kannan Sadayamuthu, Vignesh Selvam, Samuel Massé, Sheng Chen, Frank Fan, Aritra Nag, Will Childs-Klein, Praseeda Sathaye, Goutham Annem, Alexandra Huides, Jagdish Komakula, Aditya Ambati, Anand Krishna Varanasi, Angel Conde Manjon, Diego Colombatto, and Sandeep Adwankar, Manabu McCloskey, Andrew Kim, Mohit Saxena, Kartik Panjabi, Shubham Mehta, Vara Bonthu, Bikash Chandra Rout, Naga Srinivas Reddy Ravulapati, Sashikanta Pattanayak, Santiago Flores Kanter, Ravi Yadav, Hans Nesbitt, Lwanga Phillip, Swapna Bandla, Austin Groeneveld, Tarun Rai Madan, Masudur Rahaman Sayem, Adar Ovadia, Mas Kubo, Shoham Elias, Roshan Khatri, Matheus das Mercês, Moya Richards, Kenta Goto, Vivek V, Davide De Sio, Arshad Zackeriya, and Ukeme David Eseme.
Stay in touch with open source at AWS
Remember to check out the Open Source homepage for more open source goodness.
One of the pieces of feedback I received was to create a repo where all the projects featured in this newsletter are listed. Where I can hear you all ask? Well as you ask so nicely, you can meander over to newsletter-oss-projects.
Made with ♥ from DevRel