CRUD Operation in MongoDB
CRUD Operations in MongoDB
Tags: #beginners #tutorial #mongodb #database
MongoDB is a popular NoSQL database used in modern applications. Unlike relational databases, MongoDB stores data in flexible JSON-like documents, which gives you more agility in modeling real-world problems.
In this blog, we’ll walk through CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) in MongoDB using a sample “student database.” We’ll:
Insert student records
Query/filter records
Update documents
Delete documents
See how CRUD fits into typical application use
Let’s get started!
📦 Setup
First, set up your MongoDB environment (Atlas / local).
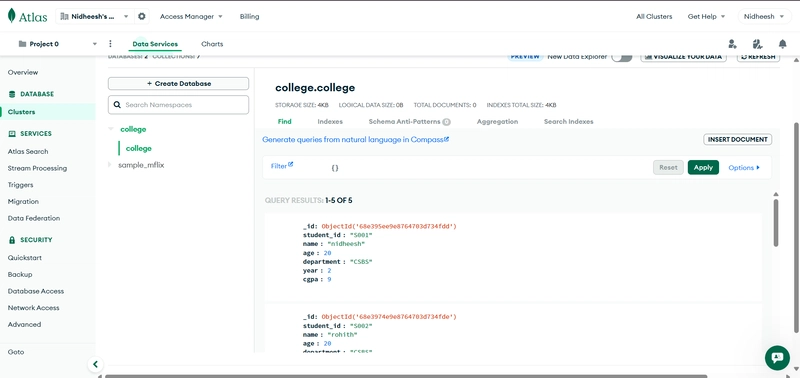
Create a database collegeDB and a collection students (or STUDENTS).
- Create (Insert)
Insert several student documents into the students collection.
// Paste your code snippet here
{
student_id: “S001”,
name: “Alice”,
age: 20,
department: “CSE”,
year: 2,
cgpa: 9.1
}
{
student_id: “S002”,
name: “Bob”,
age: 21,
department: “ECE”,
year: 3,
cgpa: 8.7
}
// more documents…
- Read (Query)
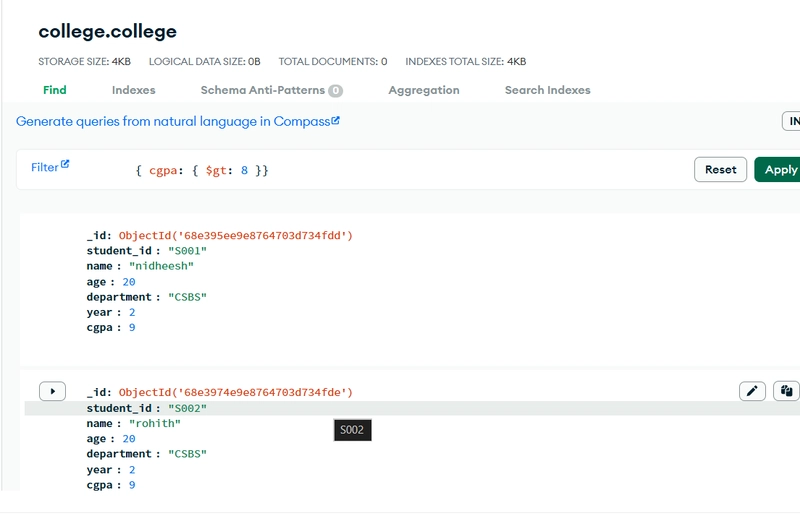
You can query documents using filters. For example:
// Find all students with CGPA > 8
db.students.find({ cgpa: { $gt: 8 } })
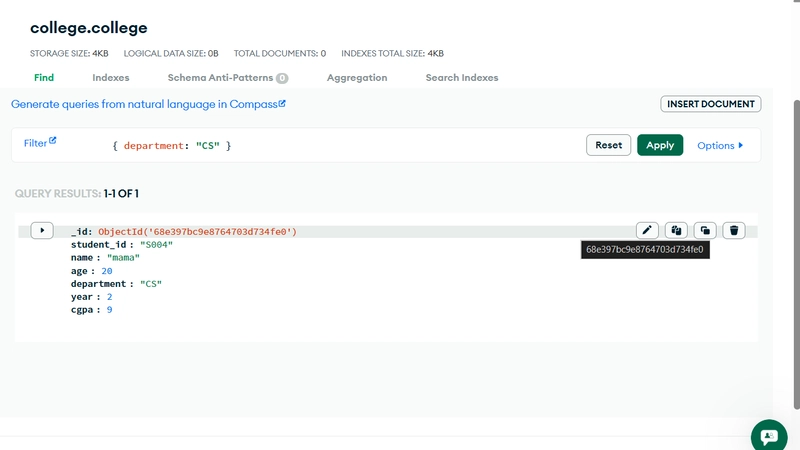
// Find all students from department “CSE”
db.students.find({ department: “CSE” })
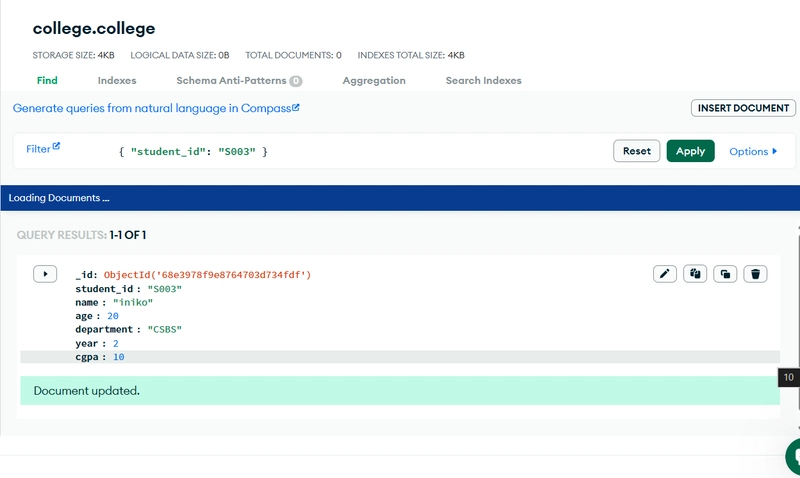
- Update
You can update one or many documents. For example:
// Update a particular student’s CGPA
db.students.updateOne(
{ student_id: “S002” },
{ $set: { cgpa: 9.0 } }
);
// Update multiple students (e.g., increment year)
db.students.updateMany(
{ year: { $lt: 4 } },
{ $inc: { year: 1 } }
);
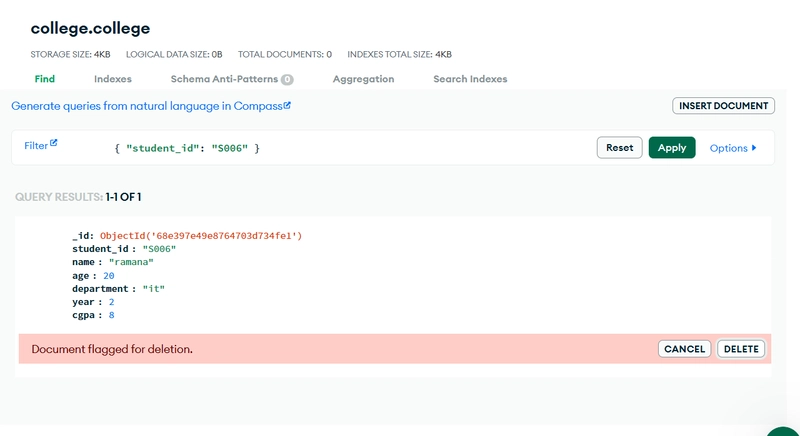
- Delete
You can remove documents that match criteria:
// Delete a specific student record
db.students.deleteOne({ student_id: “S003” });
// Delete many (e.g., all students in a certain year)
db.students.deleteMany({ year: 4 });
🏁 Conclusion
In this tutorial, we:
Inserted multiple student records
Queried/filter documents using conditions
Updated documents (single & multiple)
Deleted documents based on criteria
These CRUD operations are the foundation for most database interactions in applications — whether managing users, products, or content.